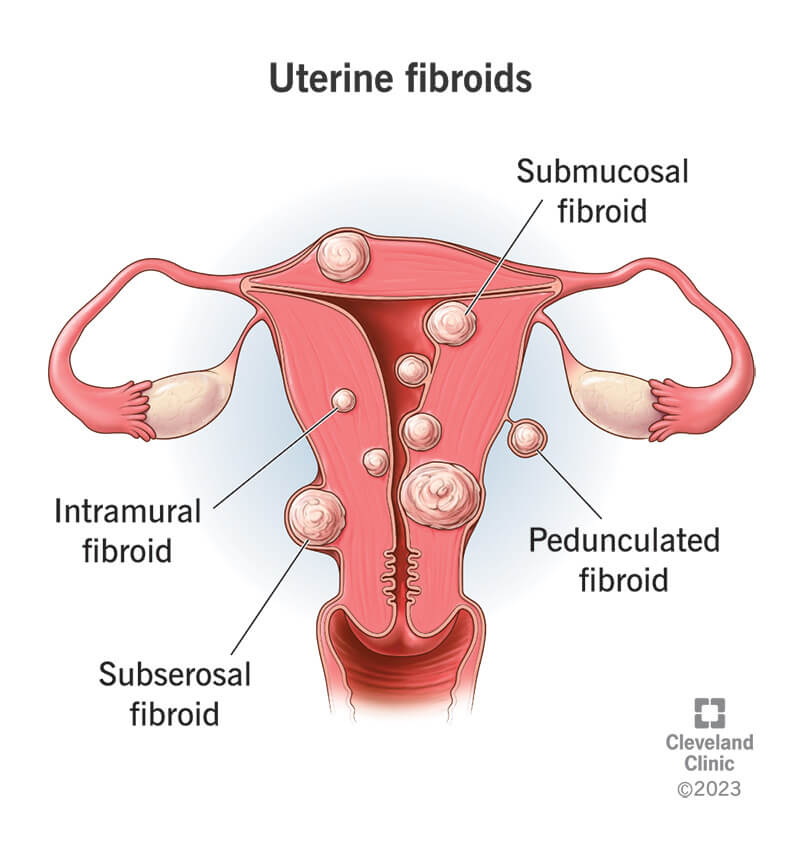
Uterine fibroids are benign (noncancerous) tumors of muscle tissue in the uterus. They are also called myomas or leiomyomas. Fibroids occur when a single muscle cell in the wall of the uterus multiplies and grows to form a noncancerous tumor. Fibroids can change the shape or size of the uterus and sometimes the cervix (lower part of the uterus). Women usually have more than one fibroid tumor but single fibroids are possible. Whether fibroids cause symptoms or require treatment depends on their location, size, and number.
Fibroids are usually found in or around the body of the uterus but sometimes are in the cervix. There are three main types of fibroids based on where they are found:
Fibroids can also be connected to the uterus by a stalk (pedunculated) or attached to nearby ligaments or organs, such as the bladder and bowel. Fibroids are rarely found outside the pelvic cavity.
Fibroids are found in 20% of women of reproductive age but are more common in African-American women (50%-80%). The exact cause of uterine fibroids is unclear, but there is evidence that it may be a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
Approximately 5% – 10% of infertile women have fibroids. Their size and location determine whether fibroids affect fertility. Examples include fibroids that are inside the uterine cavity (submucosal) or very large (>6 cm in diameter) within the wall of the uterus (intramural).
Most women with fibroids will not be infertile. Women with fibroids and their partners should be thoroughly evaluated to find other problems with fertility before fibroids are treated. A fertility specialist can help assess if fibroids might be hampering conception.
There are several ways uterine fibroids can reduce fertility:
The biggest concern in pregnancy is whether the fibroid will increase the chance of preterm birth or miscarriage. In some cases, fibroids can outgrow their blood supply and cause severe pain. Hospitalization might be needed. Also, fibroids can change the baby’s position in the uterus. This can increase the risk of miscarriage, preterm delivery, and cesarean section. How fibroids are managed depends on your unique situation and your doctor’s recommendations. Surgery is rarely necessary or performed during pregnancy.
Navigating fertility challenges can be complex, but with the right guidance and support, individuals and couples can make informed decisions to achieve their family-building goals. At Reproductive Partners Fertility Clinic in San Diego, our dedicated team is here to provide personalized care and explore fertility treatment options tailored to your unique needs.
Our skilled fertility specialists are here to help. Contact us today and let’s discuss the next phase of your fertility journey.